Scalable React Architecture: Redux, Sagas & Services Pattern
Enterprise-Grade React Application Structure with Redux Toolkit and Sagas

importantHistorical Reference (2019 Patterns): This article describes Redux patterns from 2019 using manual action creators, reducers, and redux-saga. For modern React applications in 2025, the ecosystem has evolved significantly:
- Redux Toolkit (RTK) is now the official recommended approach
- RTK Query has largely replaced redux-saga for data fetching
- Feature-based folders are more common than type-based organization
This article remains valuable for:
- Understanding and maintaining legacy Redux codebases
- Working with existing redux-saga applications
- Learning the “why” behind Redux Toolkit’s design decisions
For modern Redux development, see: Modern Redux with Redux Toolkit & RTK Query in 2025
This article is a continuation of my previous article - Architecting React Applications - where I wrote about a simple way to architect almost any React application into a modular structure. In this article, I’m going to cover a more complex codebase with application state management using Redux.
We’ll build upon the same directory structure to see if our previously prepared codebase scales well in more complex scenarios. We’ll follow the same approach: look at the directory structure, then walk through each part.
Setting Up the Basic Redux Structure
Let’s add Redux to our application to manage global state.
First, we need to set up the directory structure:
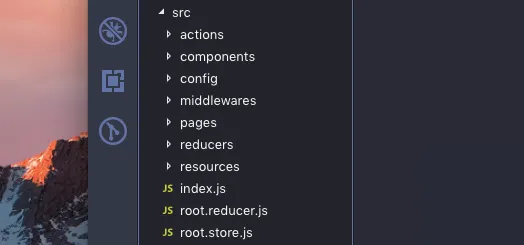
Directory Organization Rationale
This structure is one of the most popular approaches among developers and is fairly intuitive. Actions go in actions/, reducers in reducers/, and middlewares in middlewares/. What’s less common is having root.reducer and root.store files at the src root.
Many developers prefer keeping root.reducer (sometimes as index.js) inside the reducers/ directory because it’s “closer” to all the reducers. While that makes sense, I prefer keeping both at the root of src. Here’s why:
- The
reducers/directory is strictly for individual reducers. Theindex.jsinside it serves as an entry point to export all reducers. root.reducerandroot.storeare logically connected to each other rather than to individual reducers—root.reducerconfigures the reducer before hooking it up with the store (which happens inroot.store).
This makes them easier to find at the root of the src directory rather than nested. That’s why it’s named root.reducer instead of index.js—it’s meant to be discoverable.
Actions and Middlewares Structure
Similarly, our actions/ directory contains all our actions, an action.types file for all action types (you could also put this in a shared/ directory in src), and a main entry file that exports everything. Each file inside actions/ contains a set of related actions—for example, user actions, UI state actions, or data sync actions. The same pattern applies to middlewares/, which holds custom middlewares and a single entry point.
noteAll three new directories have a main entry point that exports their contents—this keeps imports cleaner and makes the structure feel more modular.
That covers the basics for any React application implementing centralized state management (and yes, you can follow similar patterns without Redux!).
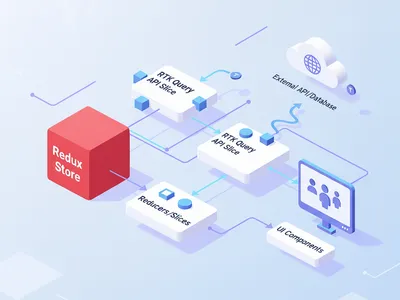
Integrating Sagas, Services, and Selectors
Let’s add more complexity to the codebase. In real-world applications with considerable scale, you typically have asynchronous actions running in parallel. For this example, let’s assume we need redux-saga for handling async operations.
We’ll also add:
- Services - for API calls and external integrations
- Selectors - for efficiently deriving data from the store (a must-have when your store gets complex)
Directory Structure
Following the same organizational pattern, we create directories for each:
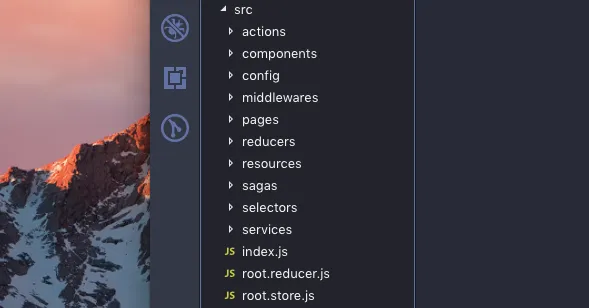
This structure is fairly self-explanatory. All sagas go in the sagas/ directory, with a root saga file inside it (you can name it root.saga or index.js)—just like the entry points in our reducers/ and actions/ directories.
Why Keep root.saga Inside the sagas/ Directory?
Here’s the reasoning: When we discussed reducers and actions, we kept their entry points as direct access points for imports. Similarly, root.saga (or index.js) in the sagas/ directory serves as an entry point that will be used in root.store during initialization. It typically contains the root saga that spawns, calls, or forks other sagas as needed.
Structure for Selectors and Services
The same pattern applies to selectors and services. Both have an entry point that exports all modules from the directory. This provides cleaner imports and a better structural overview.
Conclusion: A Scalable Foundation
This structure provides a solid foundation for complex React applications using Redux. While the ecosystem has evolved (Redux Toolkit now offers a more streamlined approach), the organizational principles here remain valuable:
- Clear separation of concerns (actions, reducers, sagas, services, selectors)
- Consistent entry points for cleaner imports
- Modular structure that scales with your application
In my experience, this type of organization scaled well across multiple projects, supporting extensive changes while keeping development productive. The patterns translate well to modern approaches—the core idea of organizing by responsibility and providing clean interfaces remains timeless.
Whether you’re maintaining a legacy codebase or learning why modern tools were designed the way they were, understanding these patterns provides valuable context for better architecture decisions.
Happy hacking! Cheers! 🎉